性能基准测试
4 分钟阅读
Benchmarking 性能基准测试
gRPC is designed to support high-performance open-source RPCs in many languages. This page describes performance benchmarking tools, scenarios considered by tests, and the testing infrastructure.
gRPC旨在支持许多语言中高性能的开源RPC。本页面介绍了性能基准测试工具、测试中考虑的场景以及测试基础架构。
Overview 概述
gRPC is designed for both high-performance and high-productivity design of distributed applications. Continuous performance benchmarking is a critical part of the gRPC development workflow. Multi-language performance tests run every few hours against the master branch, and these numbers are reported to a dashboard for visualization.
gRPC旨在实现高性能和高生产力的分布式应用程序设计。持续的性能基准测试是gRPC开发工作流程的关键部分。每隔几个小时,多语言性能测试会针对主干分支运行,并将这些数据报告给仪表板进行可视化显示。
- Multi-language performance dashboard @master (latest dev version)
- 多语言性能仪表板 @master(最新开发版本)
- Legacy dashboard (same data as above)
- 多语言性能仪表板 @master(最新开发版本)
Performance testing design 性能测试设计
Each language implements a performance testing worker that implements a gRPC WorkerService. This service directs the worker to act as either a client or a server for the actual benchmark test, represented as BenchmarkService. That service has two methods:
每种语言都实现了一个性能测试工作器,它实现了一个gRPC WorkerService。该服务指示工作器在实际的基准测试中充当客户端或服务器,表示为BenchmarkService。该服务有两个方法:
- UnaryCall – a unary RPC of a simple request that specifies the number of bytes to return in the response.
- StreamingCall – a streaming RPC that allows repeated ping-pongs of request and response messages akin to the UnaryCall.
- UnaryCall - 一个简单请求的一元RPC,该请求指定要在响应中返回的字节数。
- StreamingCall - 允许重复的请求和响应消息之间的类似UnaryCall的ping-pong的流式RPC。
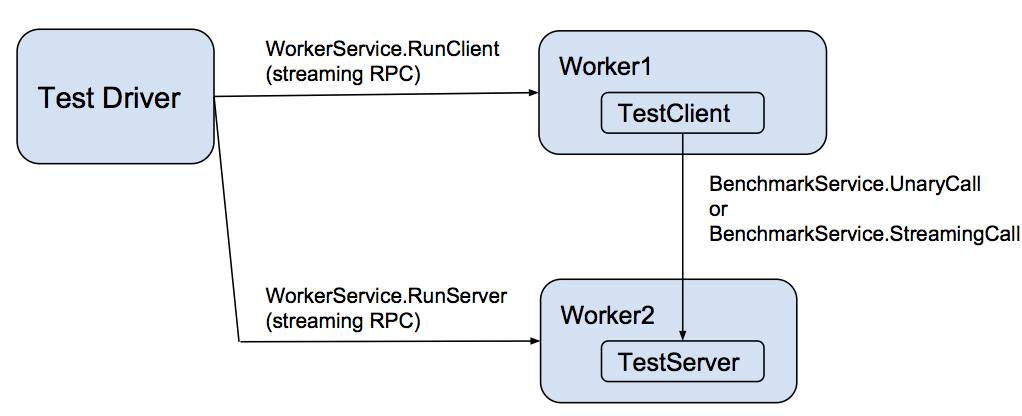
These workers are controlled by a driver that takes as input a scenario description (in JSON format) and an environment variable specifying the host:port of each worker process.
这些工作器由一个驱动程序控制,该驱动程序以JSON格式的场景描述和一个环境变量作为输入,该环境变量指定每个工作器进程的主机:端口。
Languages under test 测试的语言
The following languages have continuous performance testing as both clients and servers at master:
以下语言在主干分支上都具有连续的性能测试,既作为客户端也作为服务器:
- C++
- Java
- Go
- C#
- Node.js
- Python
- Ruby
In addition to running as both the client-side and server-side of performance tests, all languages are tested as clients against a C++ server, and as servers against a C++ client. This test aims to provide the current upper bound of performance for a given language’s client or server implementation without testing the other side.
除了作为性能测试的客户端和服务器的一侧外,所有语言都作为客户端针对C++服务器进行测试,并作为服务器针对C++客户端进行测试。此测试旨在为给定语言的客户端或服务器实现提供当前性能的上限,而不测试另一侧。
Although PHP or mobile environments do not support a gRPC server (which is needed for our performance tests), their client-side performance can be benchmarked using a proxy WorkerService written in another language. This code is implemented for PHP but is not yet in continuous testing mode.
虽然PHP或移动环境不支持gRPC服务器(这是我们性能测试所需的),但可以使用另一种语言编写的代理WorkerService来对其客户端性能进行基准测试。这段代码已经针对PHP实现,但尚未处于持续测试模式。
Scenarios under test 测试的场景
There are several important scenarios under test and displayed in the dashboards above, including the following:
上述仪表板中进行了几个重要的测试场景,包括以下内容:
- Contentionless latency – the median and tail response latencies seen with only 1 client sending a single message at a time using StreamingCall.
- QPS – the messages/second rate when there are 2 clients and a total of 64 channels, each of which has 100 outstanding messages at a time sent using StreamingCall.
- Scalability (for selected languages) – the number of messages/second per server core.
- 无竞争延迟 - 使用StreamingCall,只有一个客户端发送一条消息时的中位数和尾部响应延迟。
- QPS(每秒处理消息数) - 使用StreamingCall,当存在2个客户端和总共64个通道时,每个通道每次发送100个未完成的消息时的消息/秒率。
- 可扩展性(对于选择的语言)- 每个服务器核心的每秒处理消息数。
Most performance testing is using secure communication and protobufs. Some C++ tests additionally use insecure communication and the generic (non-protobuf) API to display peak performance. Additional scenarios may be added in the future.
大多数性能测试使用安全通信和protobuf。一些C++测试还使用不安全的通信和通用(非protobuf)API以显示峰值性能。未来可能会添加其他场景。
Testing infrastructure 测试基础架构
All performance benchmarks are run in our dedicated GKE cluster, where each benchmark worker (a client or a server) gets scheduled to different GKE node (and each GKE node is a separate GCE VM) in one of our worker pools. The source code for the benchmarking framework we use is publicly available in the test-infra github repository.
所有性能基准测试都在我们专用的GKE集群中运行,其中每个基准测试工作器(客户端或服务器)被调度到不同的GKE节点(每个GKE节点是一个单独的GCE VM)中的一个工作池。我们使用的基准测试框架的源代码可在test-infra GitHub存储库中公开获取。
Most test instances are 8-core systems, and these are used for both latency and QPS measurement. For C++ and Java, we additionally support QPS testing on 32-core systems. All QPS tests use 2 identical client machines for each server, to make sure that QPS measurement is not client-limited.
大多数测试实例都是8核系统,用于延迟和QPS测量。对于C++和Java,我们还支持在32核系统上进行QPS测试。所有QPS测试使用2台相同的客户机进行每个服务器的测试,以确保QPS测量不受客户端限制。